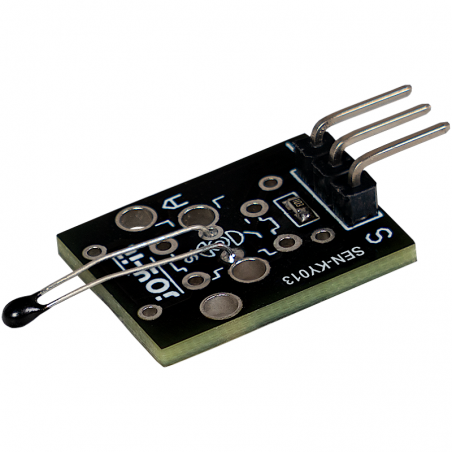



This module contains an NTC thermistor that can measure temperatures in the range from -55°C to +125°C. An NTC thermistor (Negative Temperature Coefficient) has the property that its resistance decreases as the temperature increases. This change in the resistance value makes it possible to calculate the corresponding temperature.
If you have any questions on this product please feel free to contact us.
*Disclaimer: The images are merely illustrative.
This module contains an NTC thermistor that can measure temperatures in the range from -55°C to +125°C. An NTC thermistor (Negative Temperature Coefficient) has the property that its resistance decreases as the temperature increases. This change in the resistance value makes it possible to calculate the corresponding temperature.
The relationship between temperature and resistance is not linear, but can be approximated mathematically. The change in resistance can be determined by using a voltage divider. A voltage divider consists of a known fixed resistance and the variable resistance of the thermistor. When a voltage is applied to the voltage divider, the voltage is divided according to the resistance values. By measuring the voltage across the thermistor, the current resistance can be calculated.
These resistance values can then be converted into temperatures. The exact calculation method and the mathematical approach for determining the temperature are described in the enclosed code examples. This module is ideal for applications where precise temperature measurements are required, such as in climate controls, monitoring systems and other temperature-dependent processes. Due to its high accuracy and wide measuring range, it offers a reliable solution for many temperature measurement tasks.
|
Technical Data |
|
|---|---|
|
Operating voltage |
3,3 V - 5 V |
|
Measuring range |
-55 °C to +125 °C |
|
Measurement accuracy |
± 0,5 °C |
|
Known resistance |
10 kΩ |
|
Specific resistance of the NTC |
3950 Ω |
|
Arduino |
Sensor |
|---|---|
|
A1 |
Signal |
|
5 V |
+V |
|
GND |
GND |
The program measures the current voltage value at the NTC, calculates the temperature and translates the result to °C for serial output.
To load the following code example onto your Arduino, we recommend using the Arduino IDE. In the IDE, you can select the appropriate port and board for your device.
Copy the code below into your IDE. To upload the code to your Arduino, simply click on the upload button.
int ntc = A1; // Declaration of the sensor input pin
// Declaration of temporary variables
double raw_value;
double voltage;
double temperature;
void setup () {
pinMode(ntc, INPUT); // Initialization sensor pin
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialization of the serial monitor
Serial.println("KY-013 NTC temperature test");
}
void loop () {
// Read out analog value
raw_value = analogRead(ntc);
// Read out the voltage using an analog value
voltage = raw_value * 5.0 / 1023.0;
// Calculation of the temperature using the voltage
temperature = ((voltage / 5.0) * 10000.0) / (1.0 - (voltage / 5.0));
temperature = 1.0 / ((1.0 / 298.15) + (1.0 / 3950.0) * log(temperature / 10000.0));
temperature = temperature - 273.15;
// Output of the measured value
Serial.println("Temperature: " + String(temperature) + " °C");
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second for next measurement
}
Related products
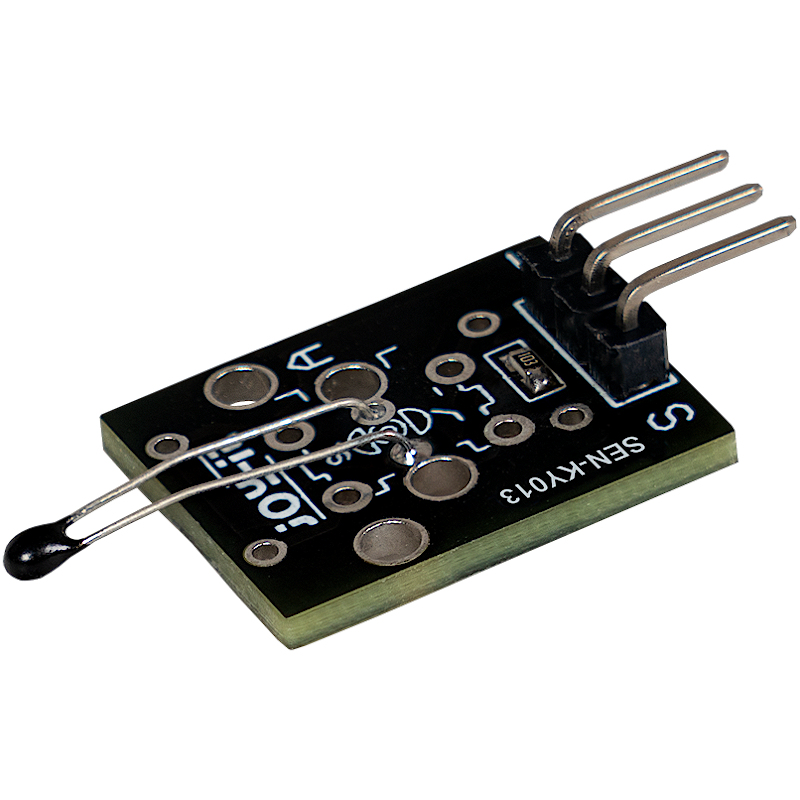
This module contains an NTC thermistor that can measure temperatures in the range from -55°C to +125°C. An NTC thermistor (Negative Temperature Coefficient) has the property that its resistance decreases as the temperature increases. This change in the resistance value makes it possible to calculate the corresponding temperature.

